Description
THE TALMUD in Urdu language / تلمود۔ / Pakistan
- Hardcover 2018
- Pages 238
- Publisher: Pakistan Bible Society
- Language: Urdu
Description:
The Talmud is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law and tradition. It is a collection of debates and commentaries on the Mishnah, a compilation of Jewish law and tradition dating from the 2nd century CE. The Talmud was compiled between the 3rd and 8th centuries CE in two major recensions, the Babylonian Talmud and the Jerusalem Talmud.
The Urdu translation of the Talmud was published in 2018 by the Pakistan Bible Society. It is a hardcover book with 238 pages.
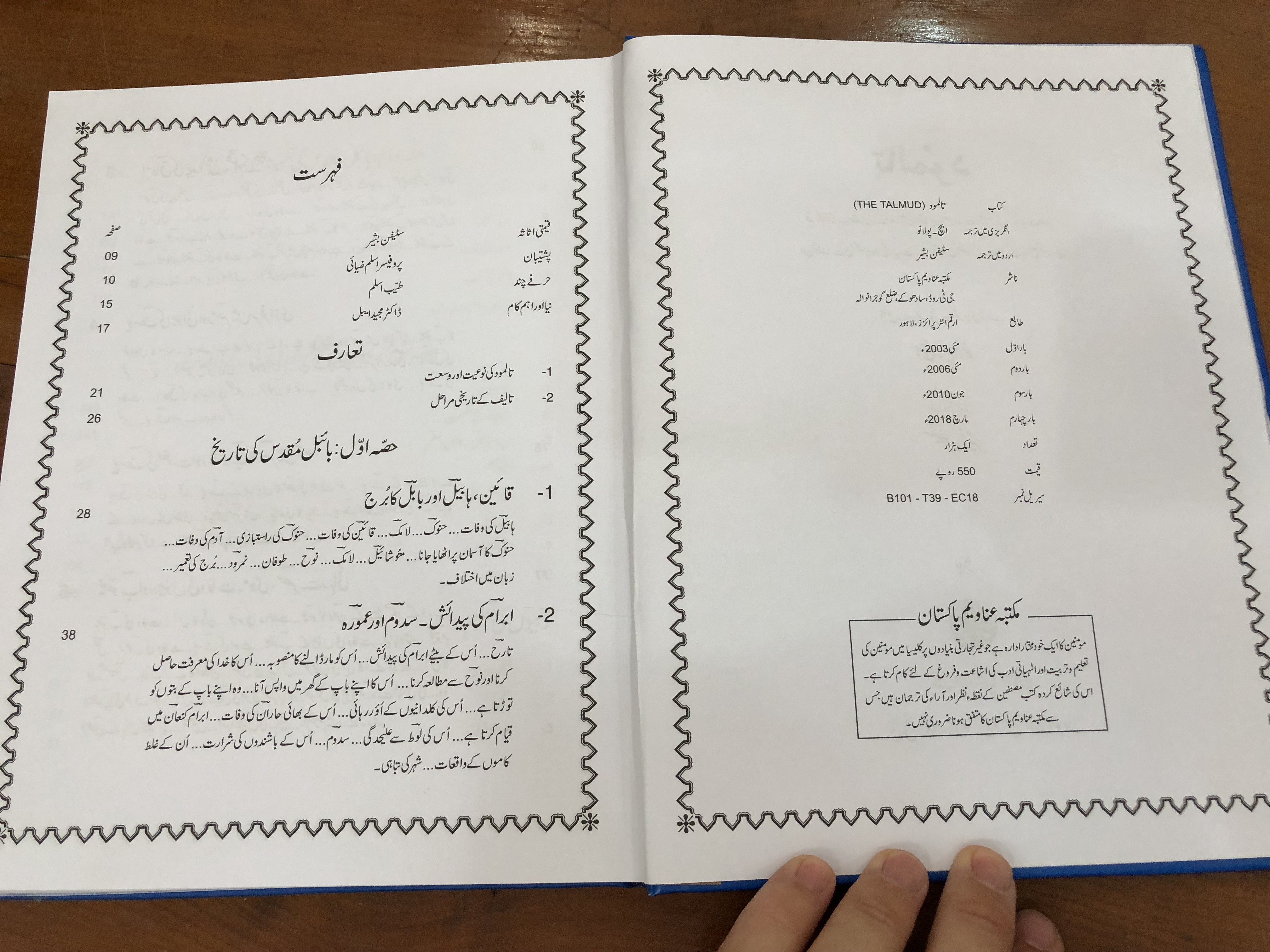
The translation was made by Stephen Basheer, who translated it from English to Urdu. The English translation was made by Professor H. Polano, a Professor of Hebrew Language.
The Urdu translation of the Talmud is a valuable resource for Urdu-speaking Jews and scholars of Judaism. It makes the Talmud accessible to a wider audience and allows for a deeper understanding of Jewish law and tradition.
تفصیل: تلمود رابنی یہودیت کا وسطائی متن ہے اور یہودی مذہبی قوانین اور روایات کی بنیادی سرچشمہ ہے۔ یہ دوسویں بحثوں اور مشناہ پر تبصرے کا مجموعہ ہے جو دوسری صدی عیسوی میں یہودی قانون اور روایات کا مجموعہ تھا۔ تلمود تینویں اور آٹھویں صدیوں عیسوی میں دو بڑی قسموں میں مصنوع تھا، بابلی تلمود اور اورشلیمی تلمود۔
تلمود کا اردو ترجمہ پاکستان بائبل سوسائٹی کی جانب سے 2018ء میں شائع کیا گیا تھا۔ یہ ایک سخت کاور کتاب ہے جس میں 238 صفحات ہیں۔
اس ترجمہ کا مترجم سٹیفن بشیر ہے جنہوں نے اسے انگریزی سے اردو میں ترجمہ کیا تھا۔ انگریزی ترجمہ پروفیسر ایچ۔پولانو نے کیا تھا جو عبرانی زبان کے پروفیسر تھے۔
تلمود کا اردو ترجمہ اردو بولنے والے یہودیوں اور یہودیت کے علمگیران کے لئے ایک قیمتی ذریعہ ہے۔ یہ تلمود کو ایک وسیع حوالے تک پہنچانے کی اجازت دیتا ہے اور یہودی قانون اور روایات کی عمیق سمجھ کی اجازت دیتا ہے۔
English Summary:
The Talmud (/ˈtɑːlmʊd, -məd, ˈtæl-/; Hebrew: תַּלְמוּד talmūd) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (halakha) and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews.
The term "Talmud" normally refers to the collection of writings named specifically the Babylonian Talmud (Talmud Bavli), although there is also an earlier collection known as the Jerusalem Talmud (Talmud Yerushalmi). It may also traditionally be called Shas (ש״ס), a Hebrew abbreviation of shisha sedarim, or the "six orders" of the Mishnah.
The Talmud has two components; the Mishnah (Hebrew: משנה, c. year 200 CE), a written compendium of Rabbinic Judaism's Oral Torah; and the Gemara (Hebrew: גמרא, c. year 500 CE), an elucidation of the Mishnah and related Tannaitic writings that often ventures onto other subjects and expounds broadly on the Hebrew Bible. The term "Talmud" may refer to either the Gemara alone, or the Mishnah and Gemara together.
The entire Talmud consists of 63 tractates, and in standard print is 2,711 double-sided folios It is written in Mishnaic Hebrew and Jewish Babylonian Aramaic and contains the teachings and opinions of thousands of rabbis (dating from before the Common Era through to the fifth century) on a variety of subjects, including halakha, Jewish ethics, philosophy, customs, history, lore and many other topics. The Talmud is the basis for all codes of Jewish law, and is widely quoted in rabbinic literature.












































![The Children's Bible in Urdu Persian / Pakistan Children's Bible [Hardcover] The Children's Bible in Urdu Persian / Pakistan Children's Bible [Hardcover]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-62bdpkt7pb/images/stencil/590x590/products/653/1015/1__41310.1462823129.JPG?c=2)

